Rectifying Strip Patterns
Computational design and fabrication, Shading system, Gridshell,Pseudo-geodesic, Developable strips
Publication
ACM Transactions on Graphics; Accepted by the SIGGRAPH Asia 2023 conference (Dec.12-15, Sydney, Australia).
Authors
Bolun Wang, Hui Wang, Eike Schling, Helmut Pottmann
Abstract
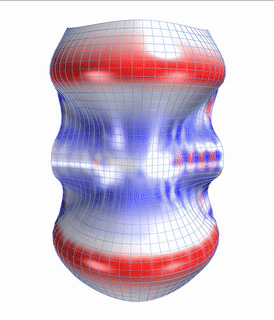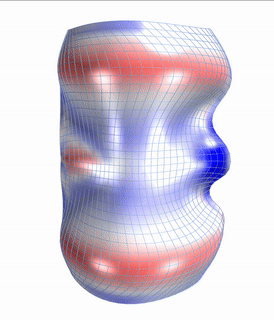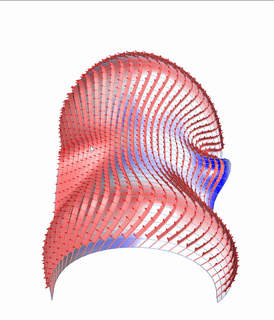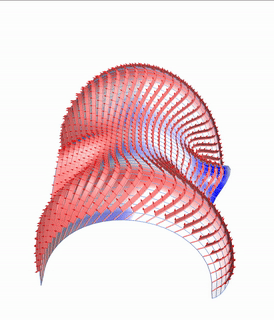
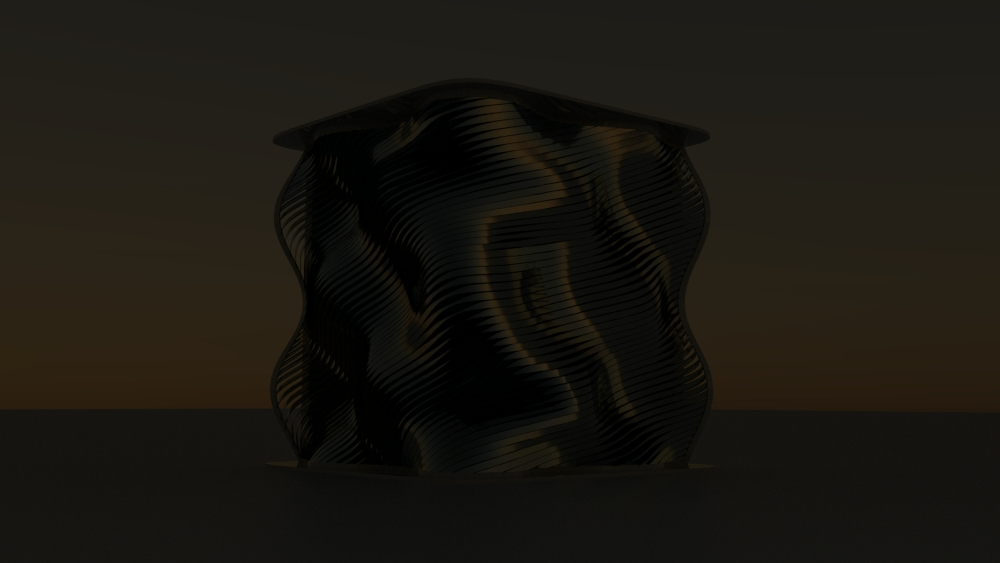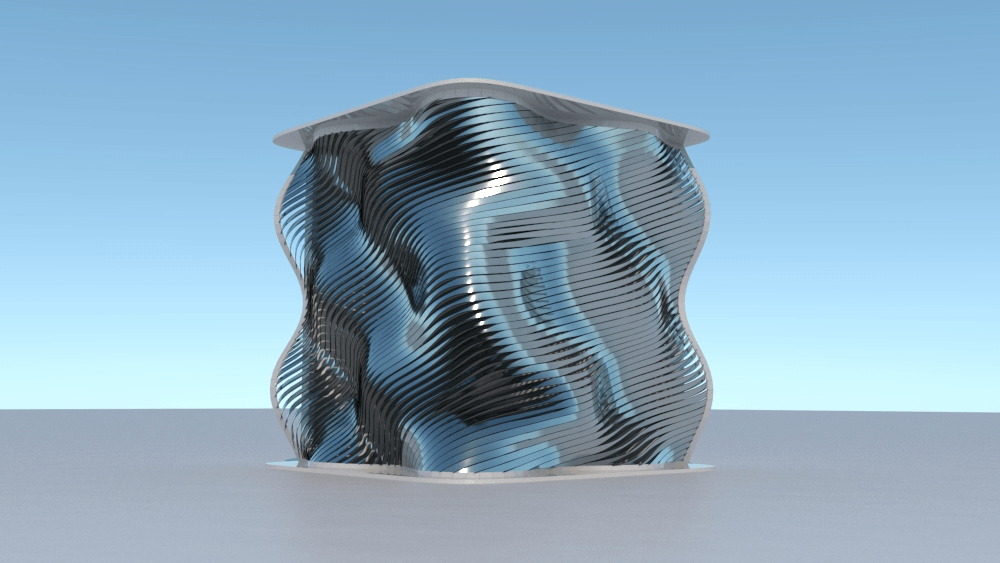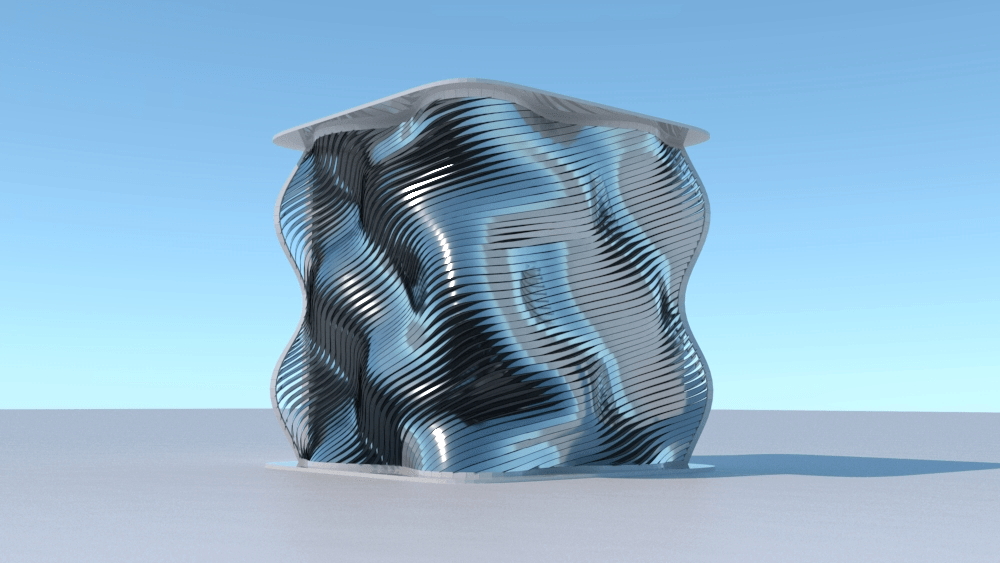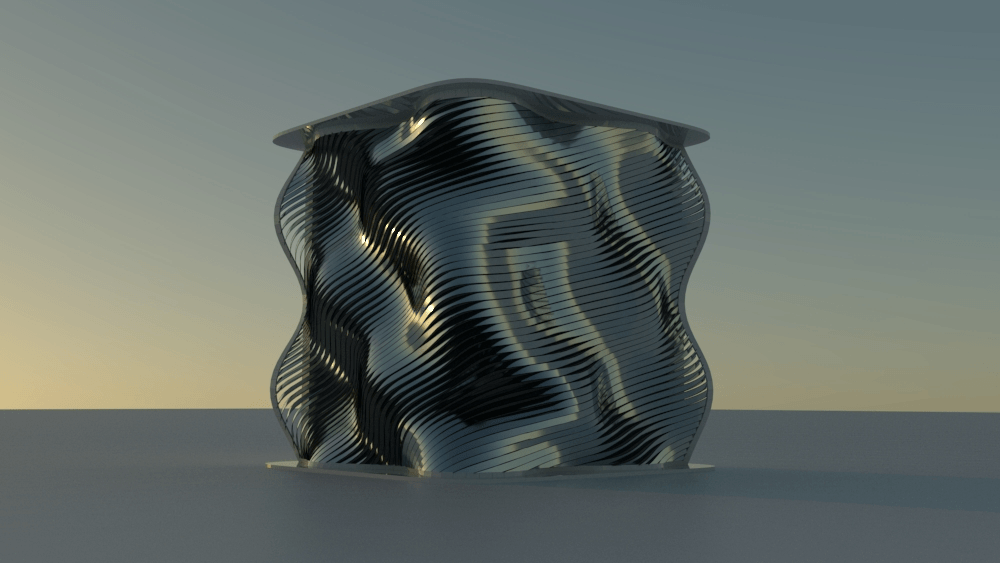
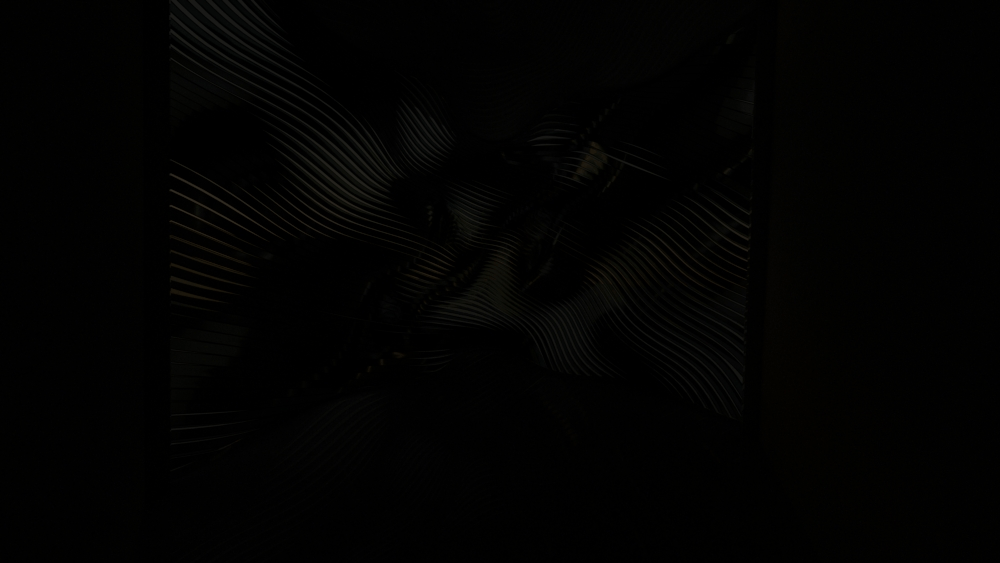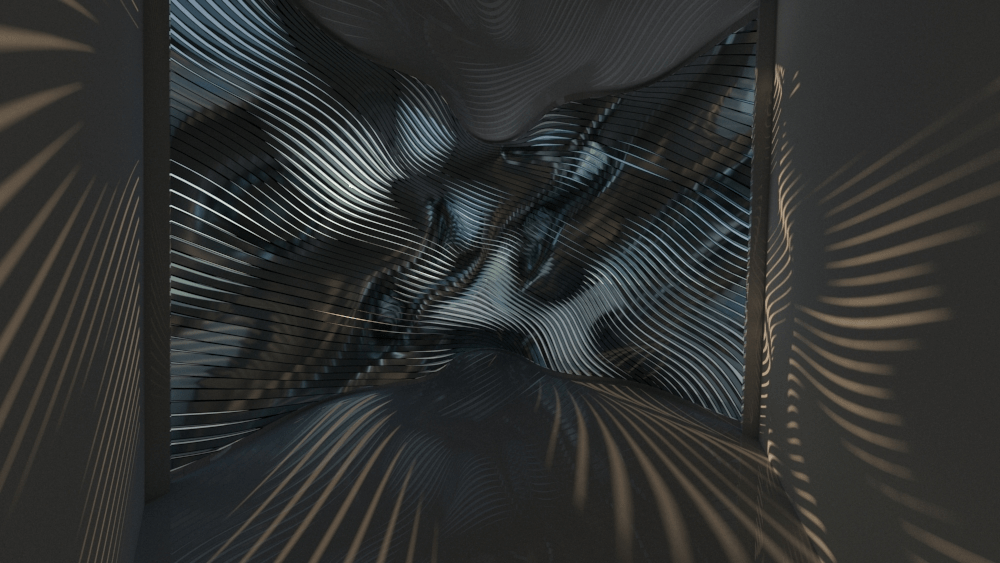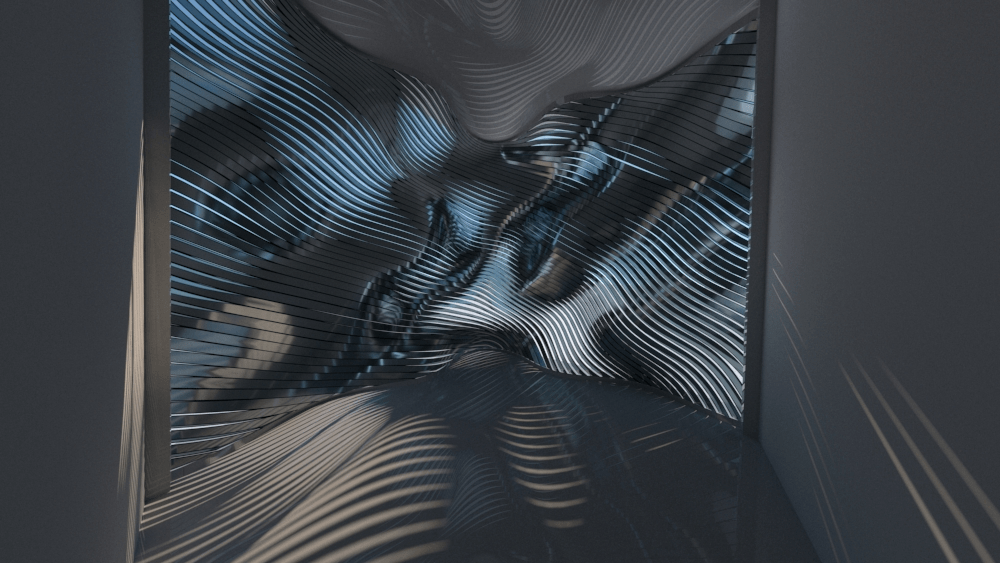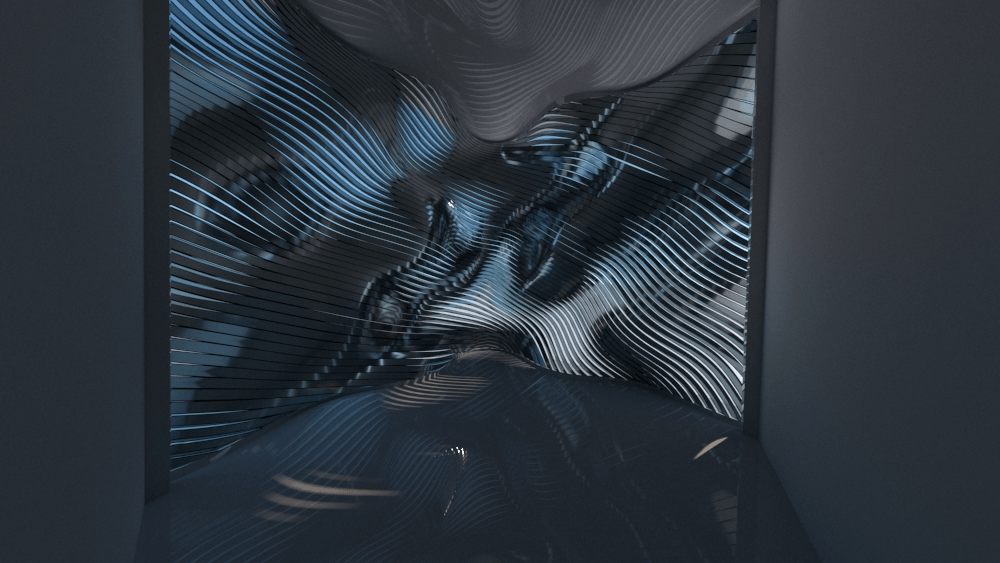
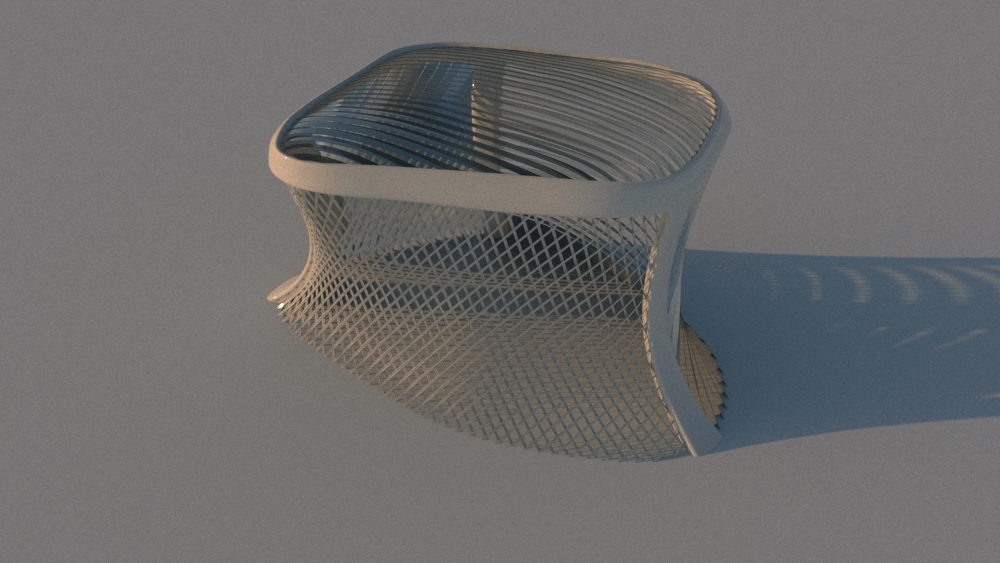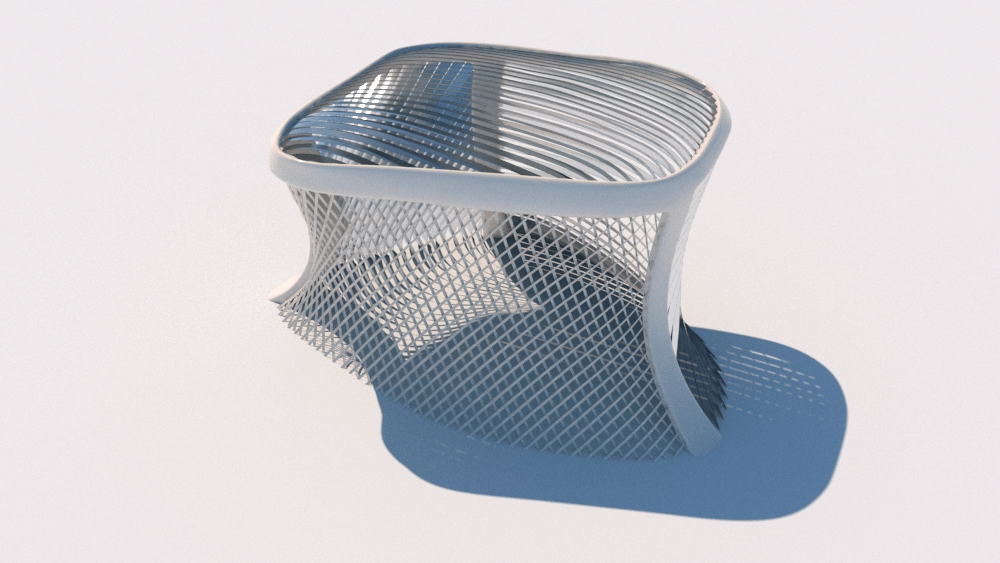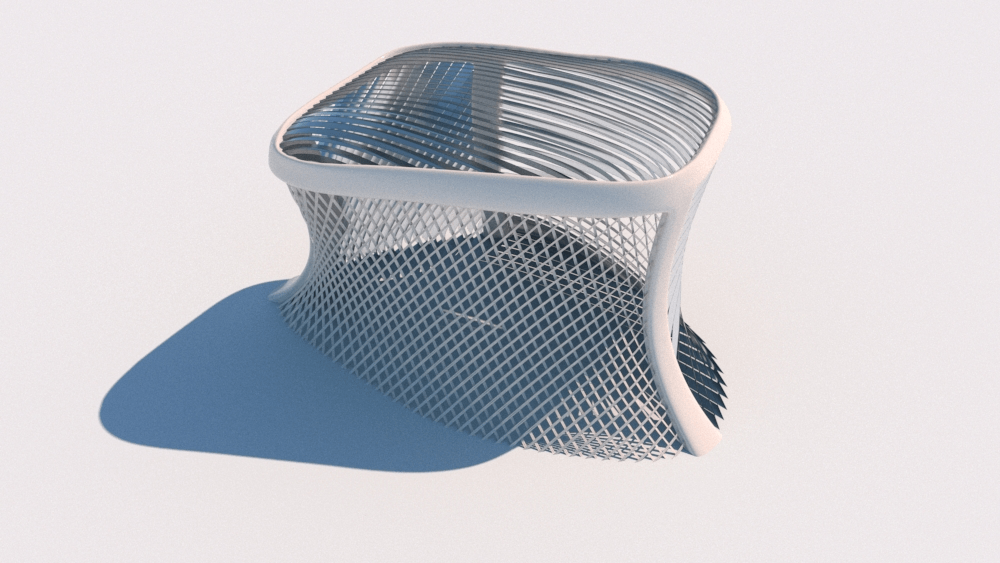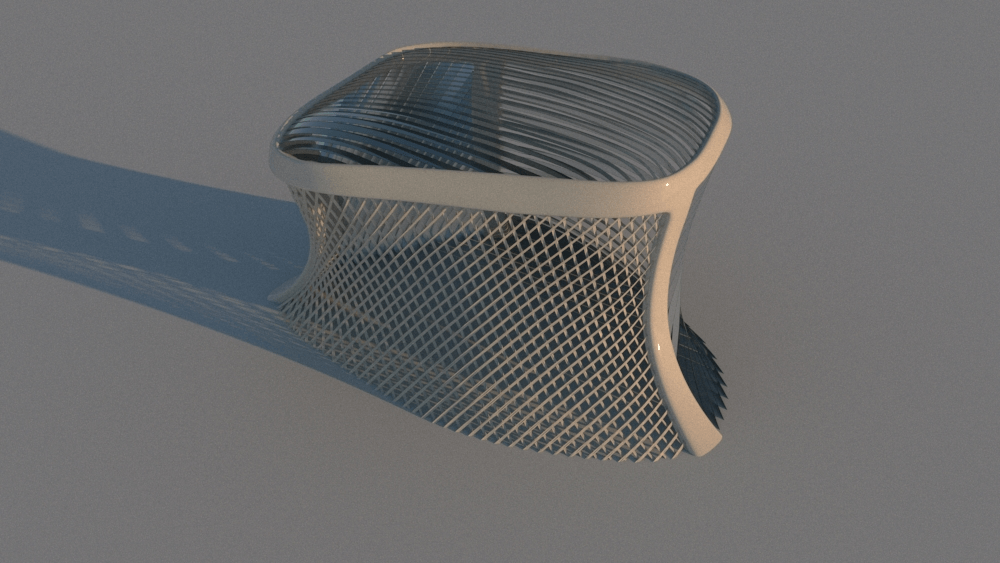
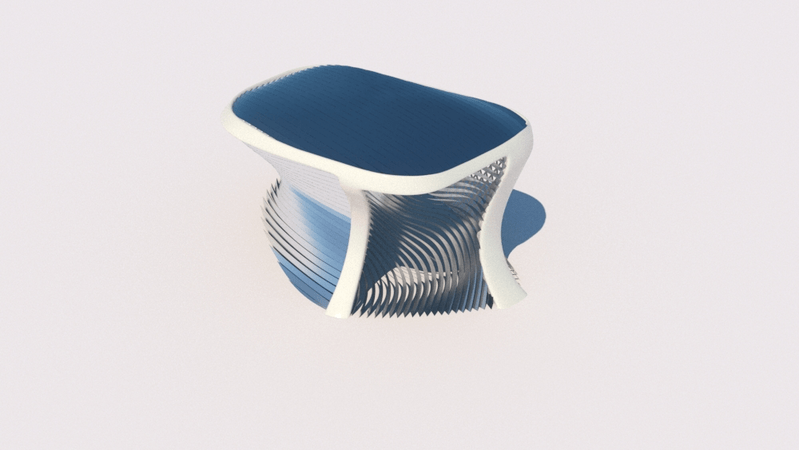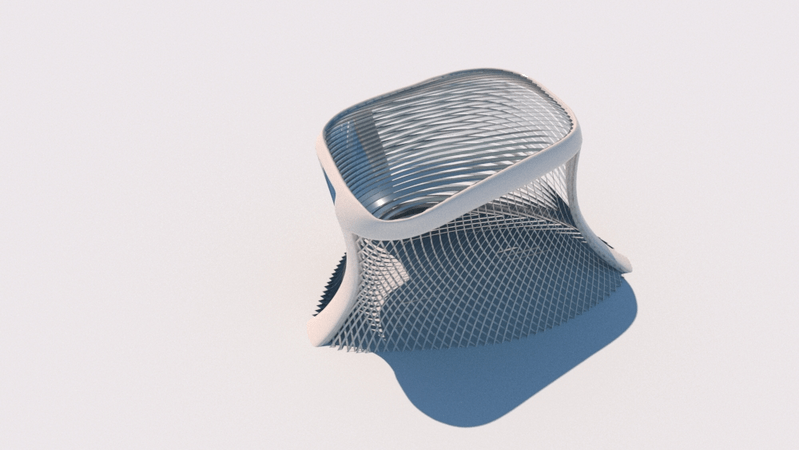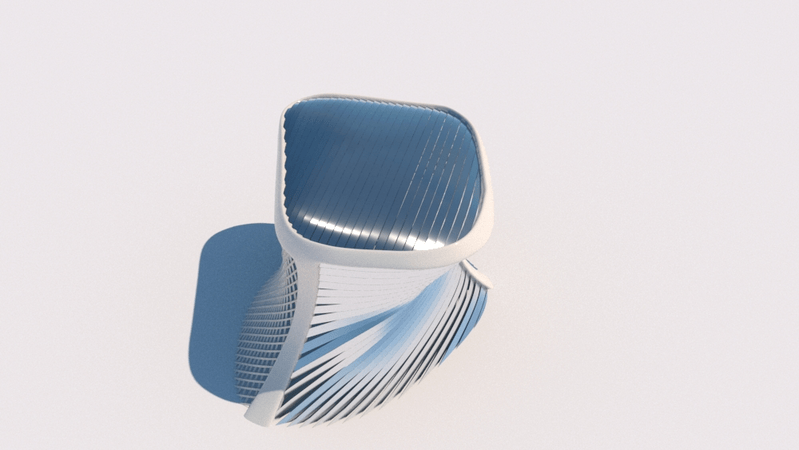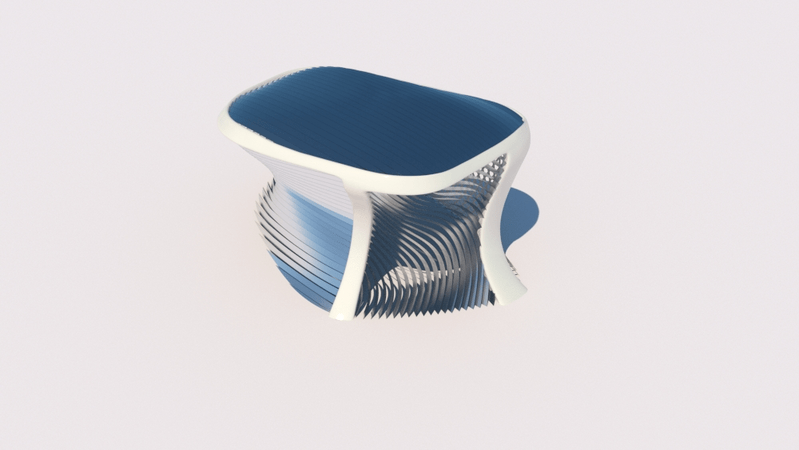
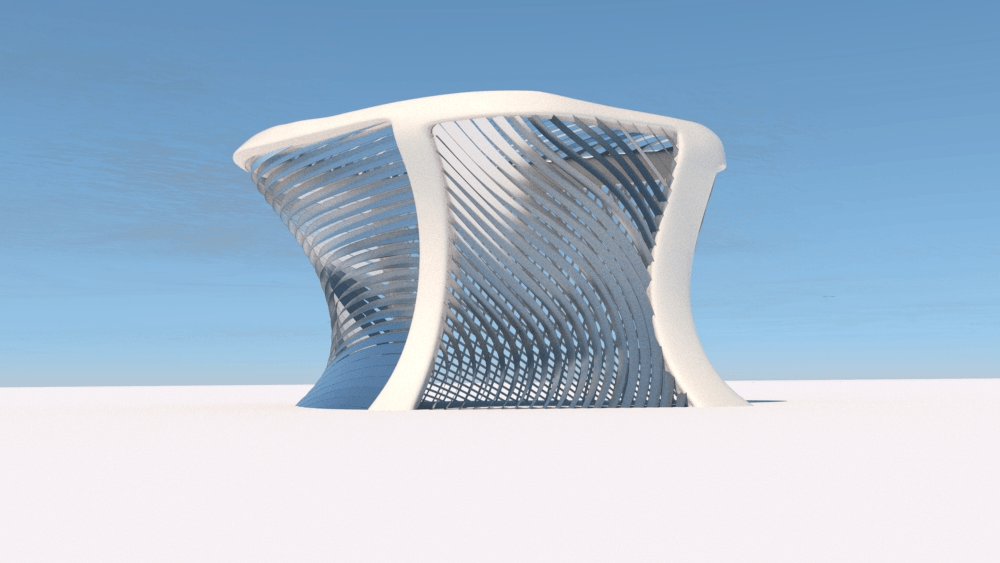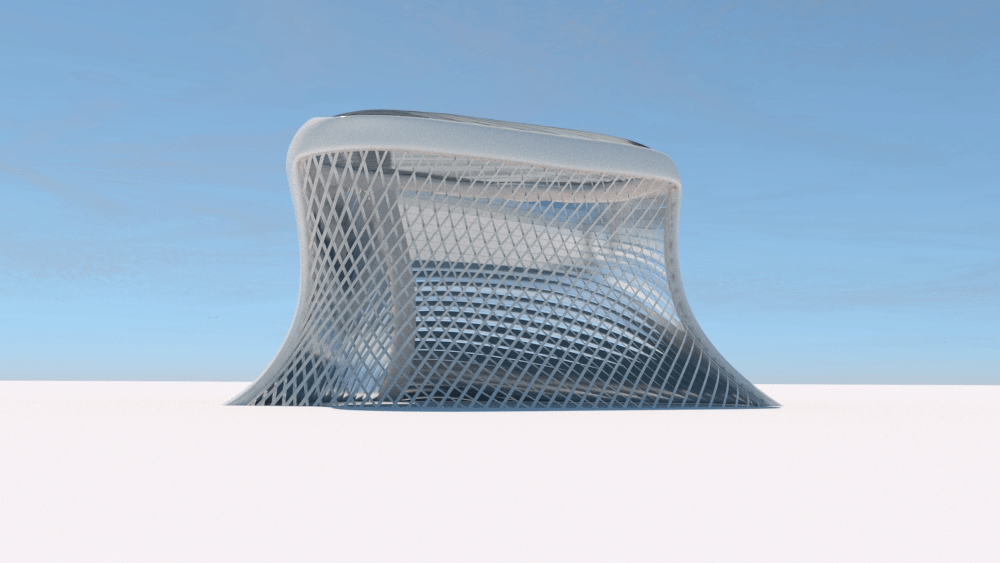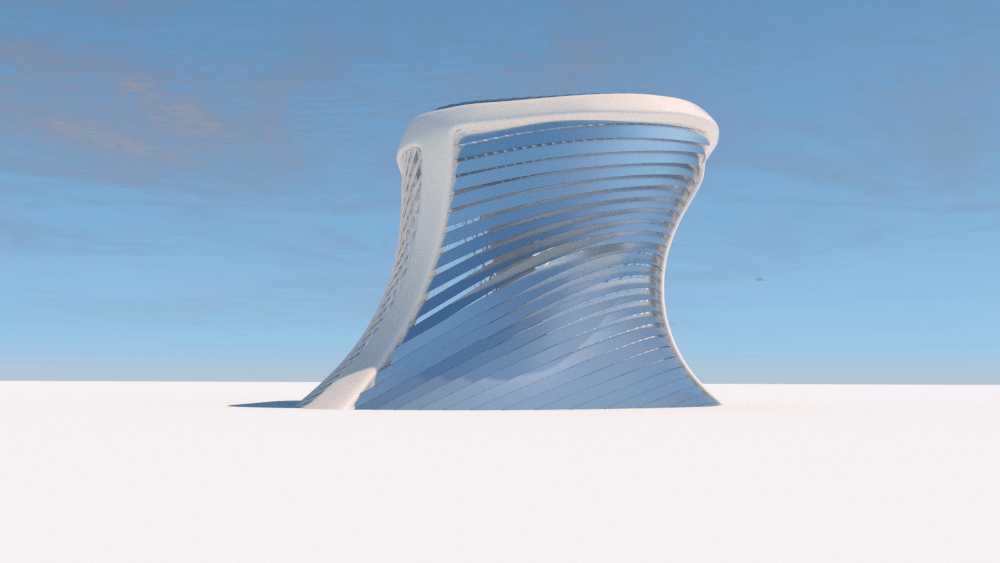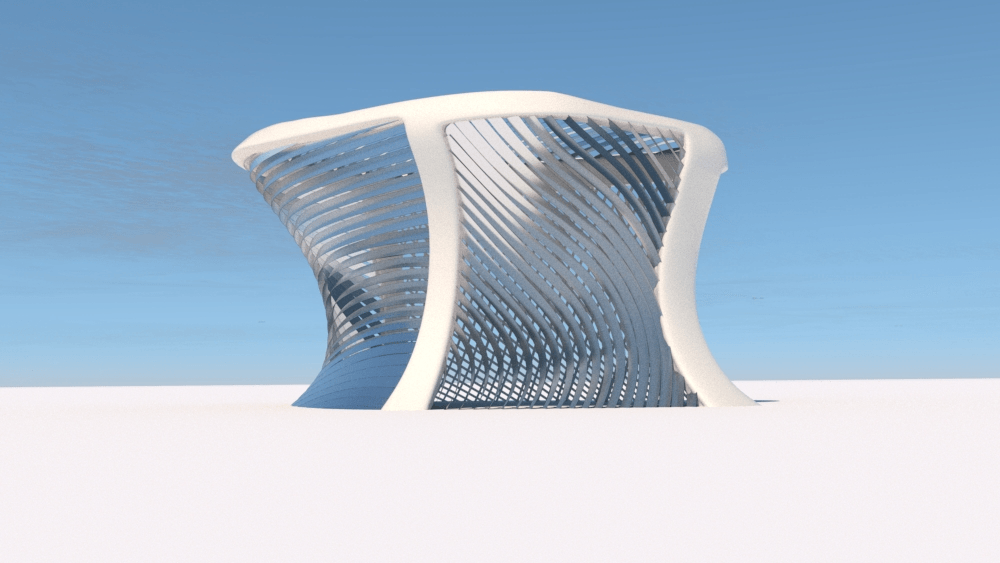
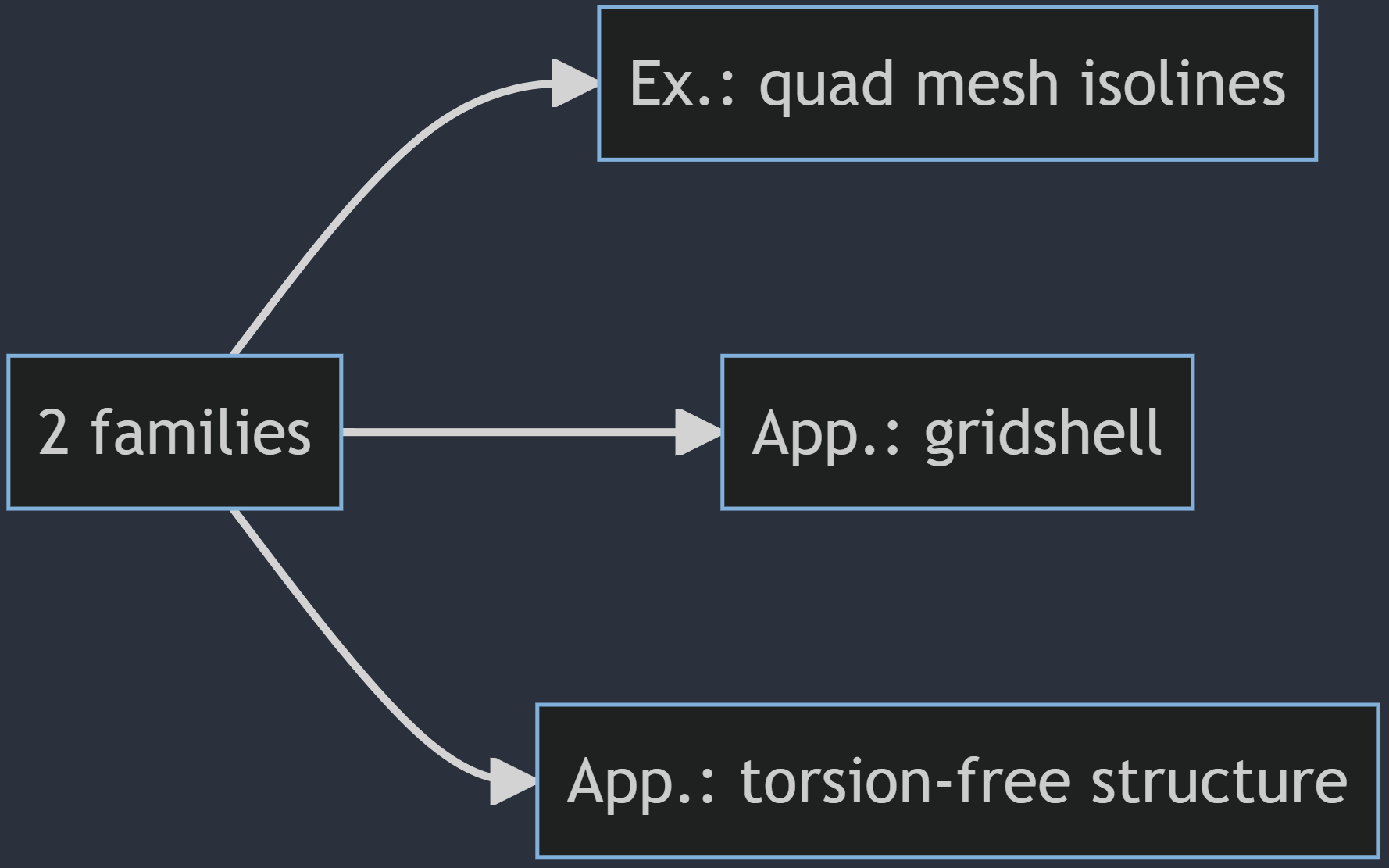
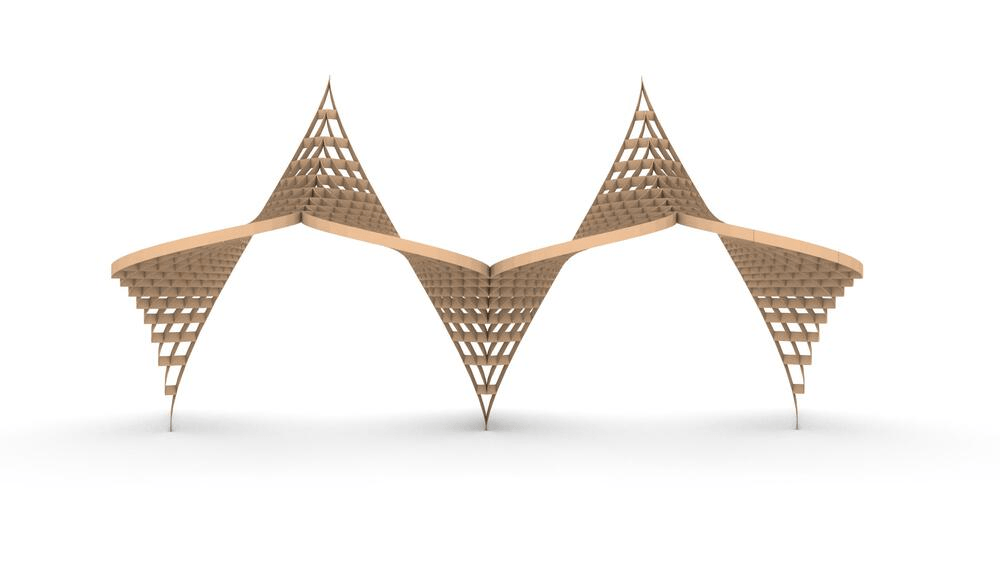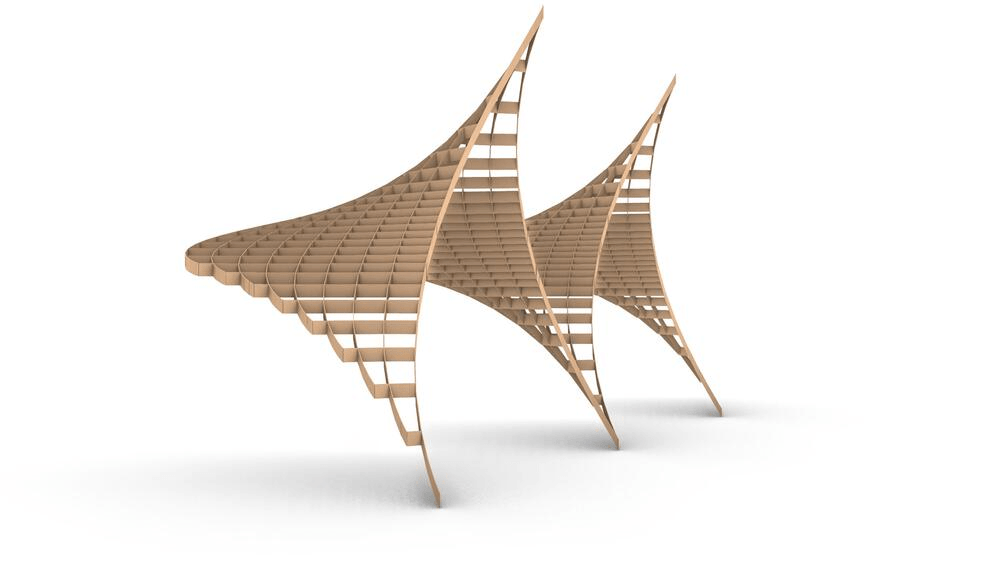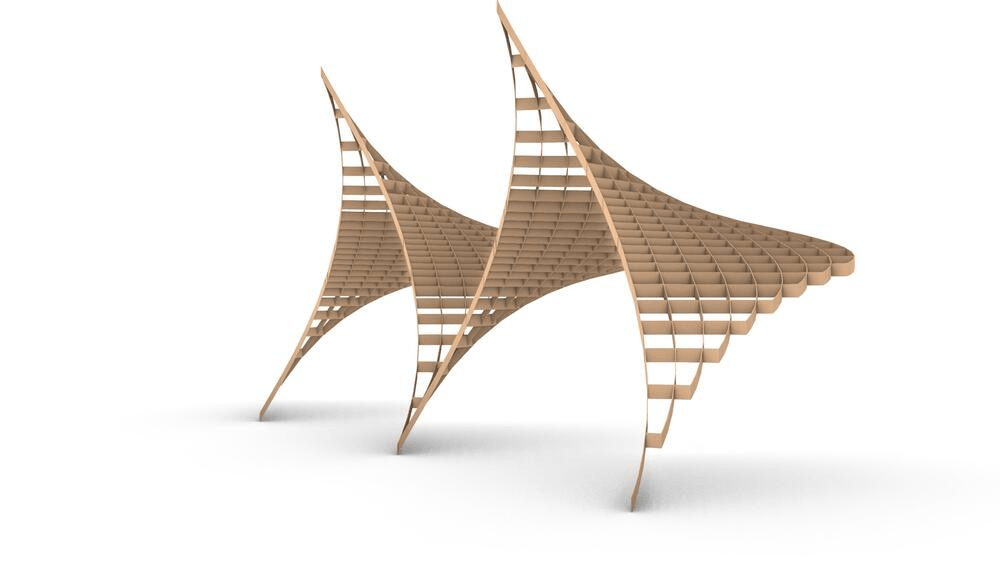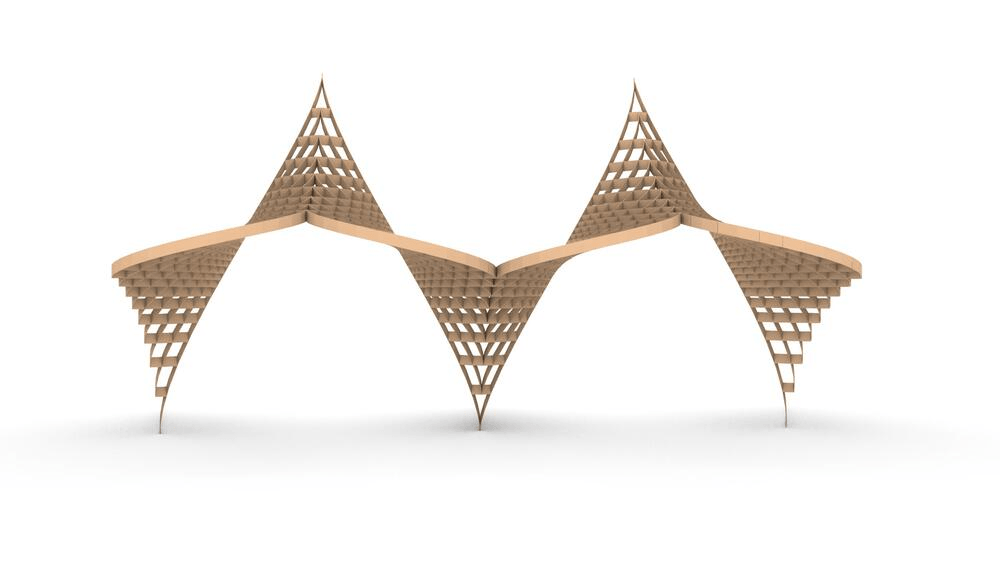
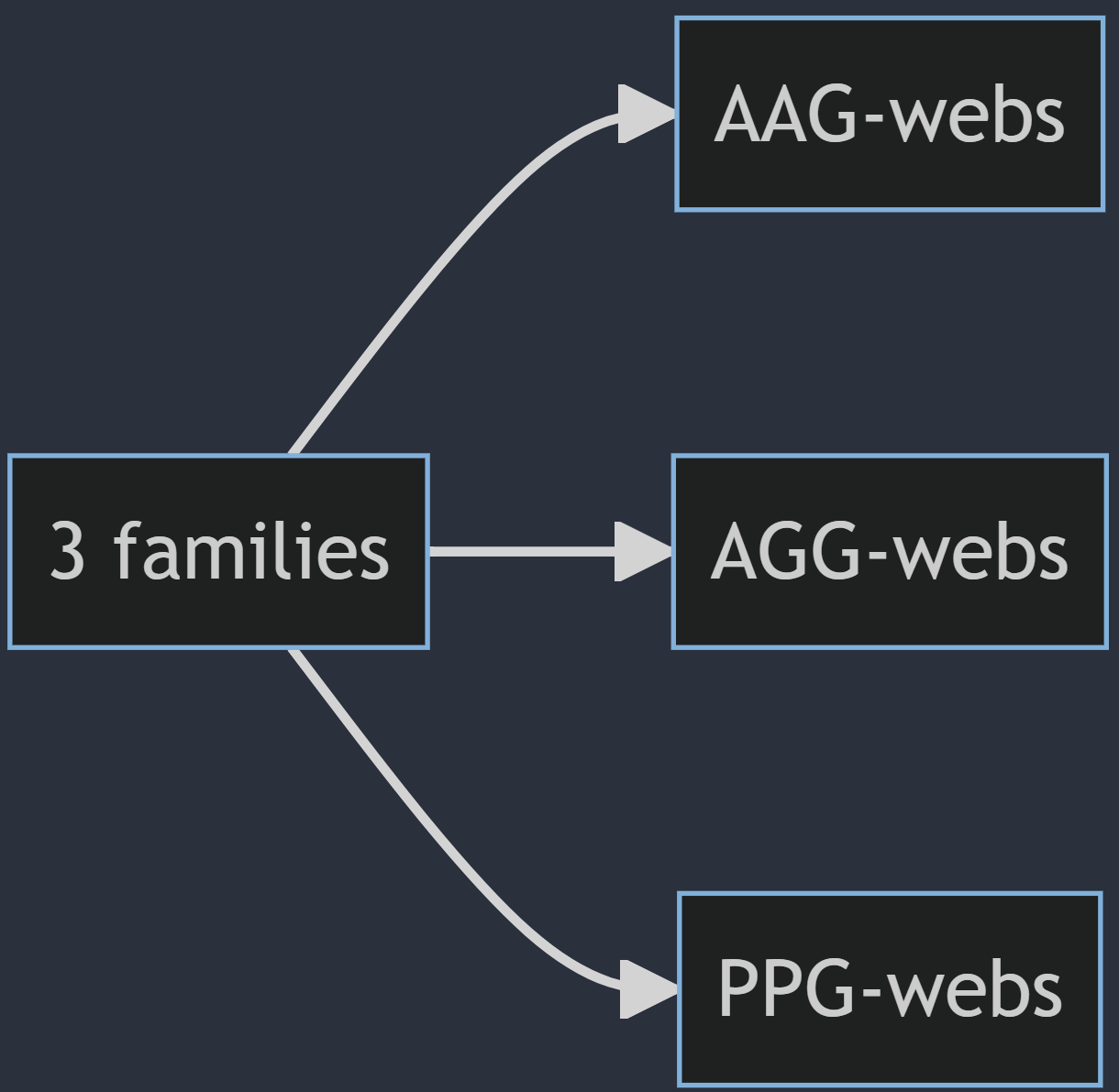
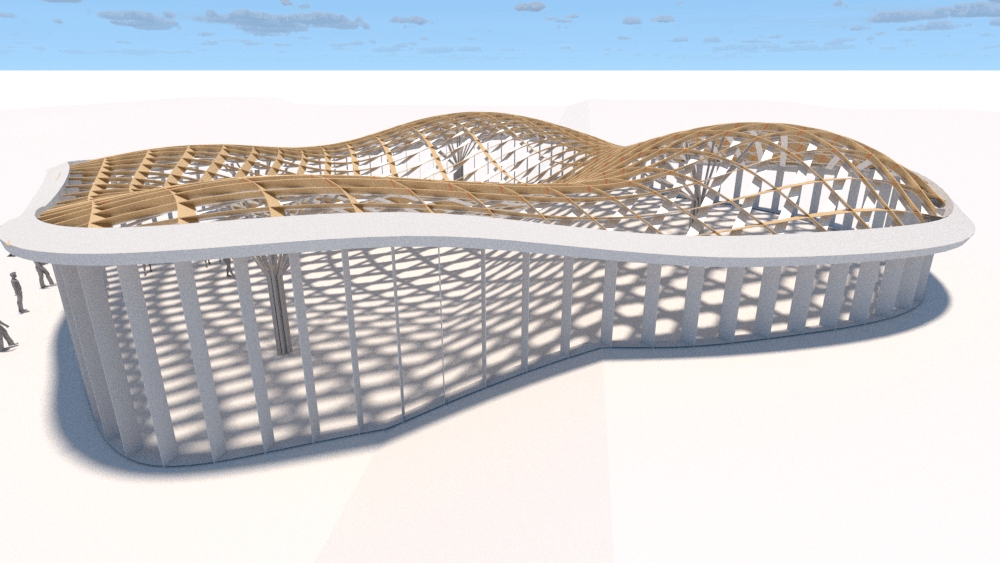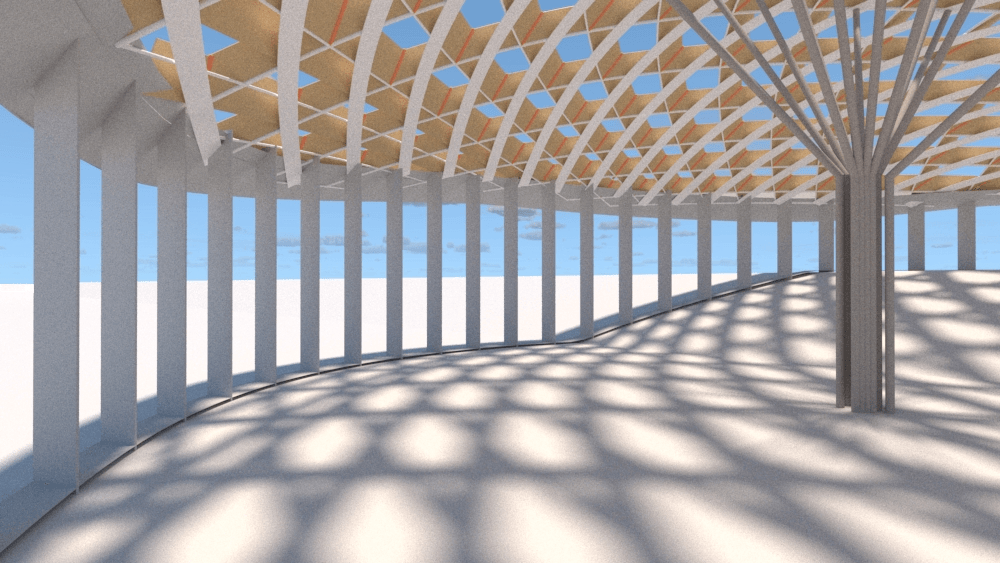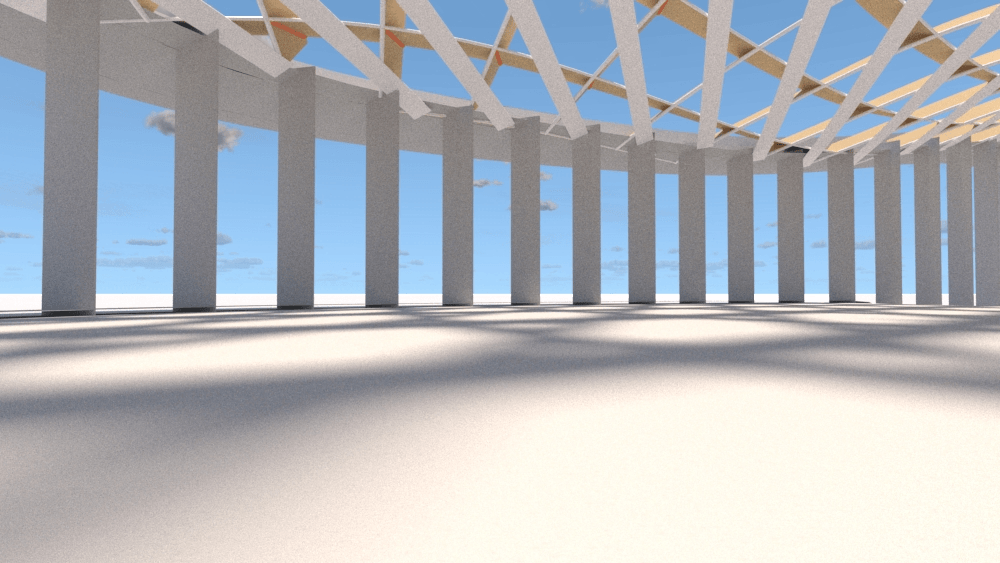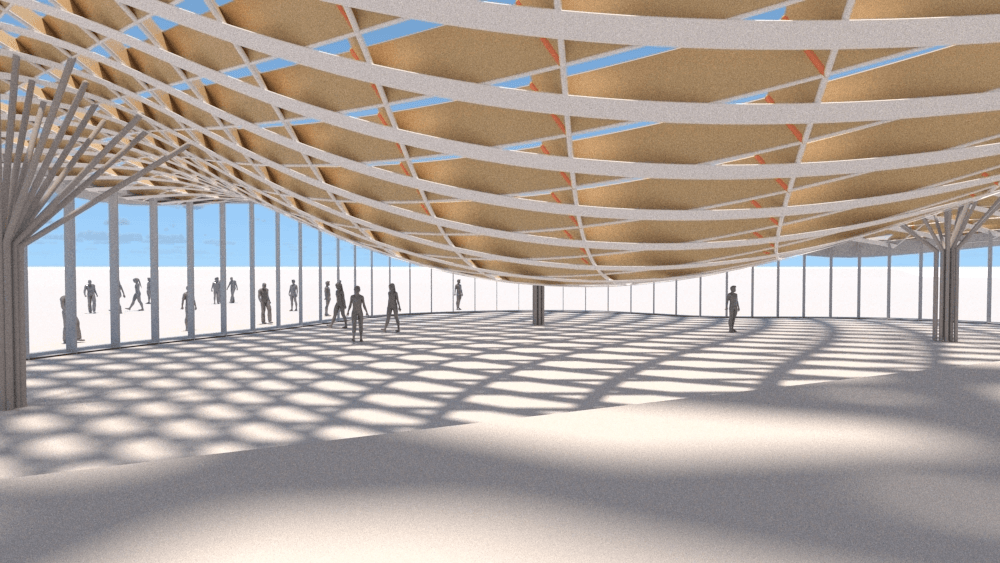
Straight flat strips of inextensible material can be bent into curved strips aligned with arbitrary space curves. The large shape variety of these socalled rectifying strips makes them candidates for shape modeling, especially in applications such as architecture where simple elements are preferred for the fabrication of complex shapes. In this paper, we provide computational tools for the design of shapes from rectifying strips. They can form various patterns and fulfill constraints which are required for specific applications such as gridshells or shading systems. The methodology is based on discrete models of rectifying strips, a discrete level-set formulation and optimization-based constrained mesh design and editing. We also analyse the geometry at nodes and present remarkable quadrilateral arrangements of rectifying strips with torsion-free nodes.
Slide
Figures
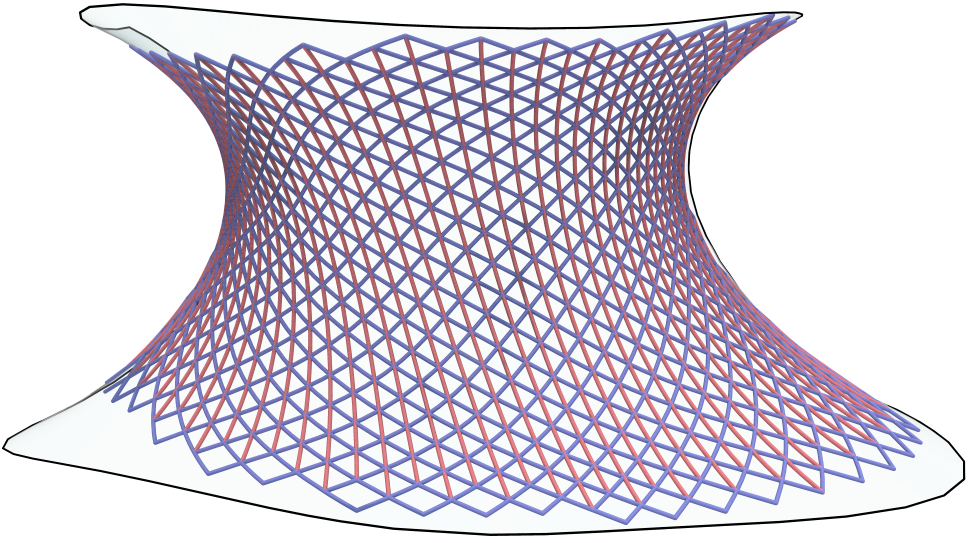
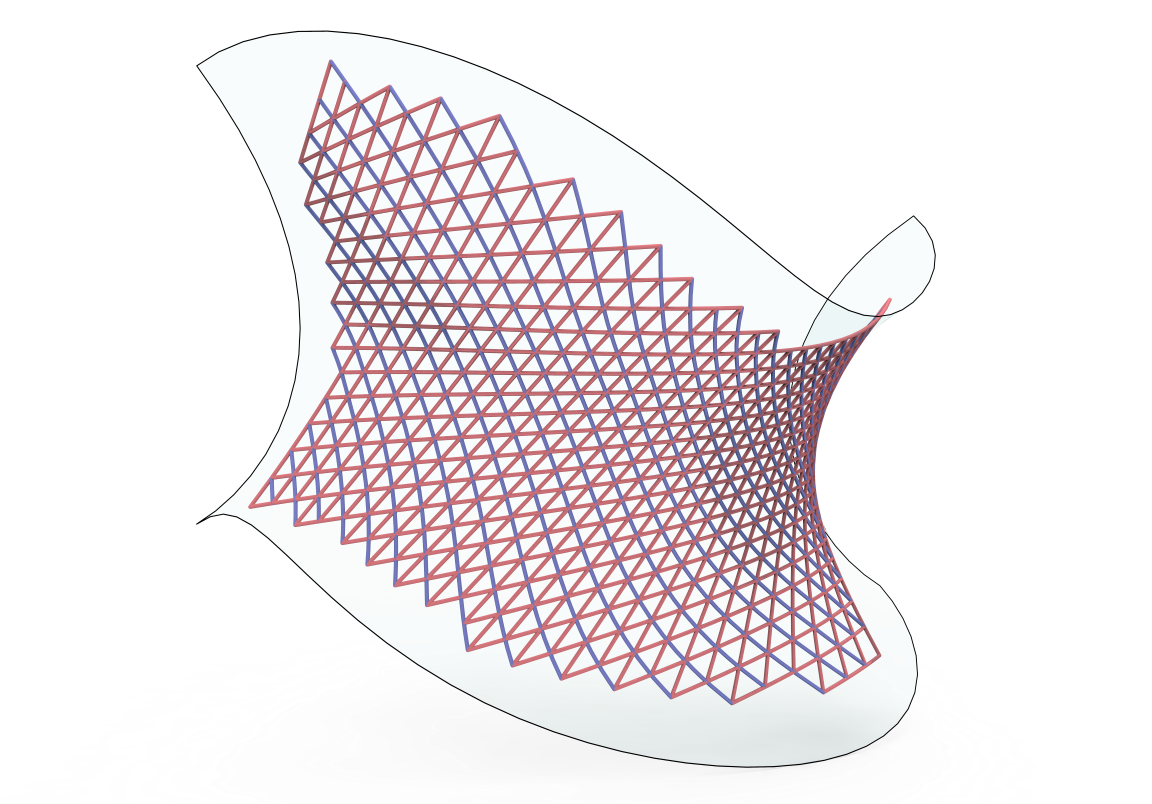
Pseudo-geodesic curves of a surface was first studied by Walter Wunderlich in 1950. They are the curves whose osculating planes have a constant angle \(\theta\) with the tangent planes of the surface. When \(\theta=90^o\), they are geodesic; when \(\theta=0^o\), they are asymptotic curves.
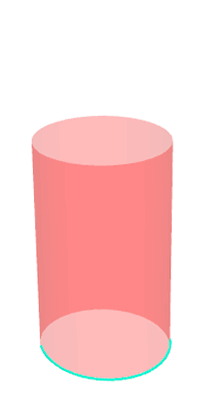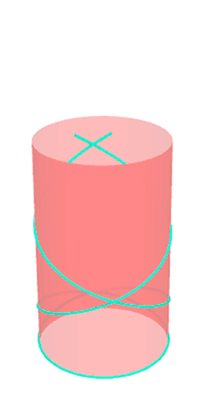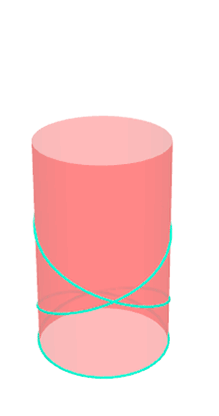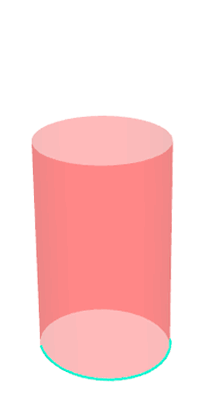
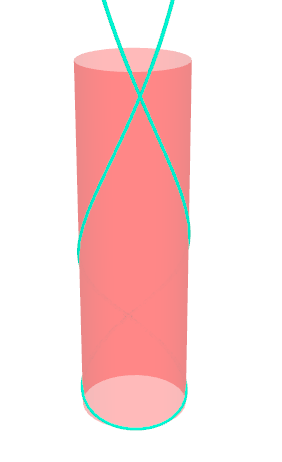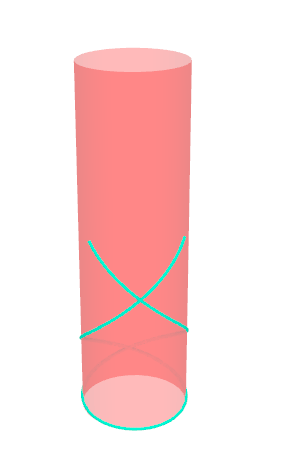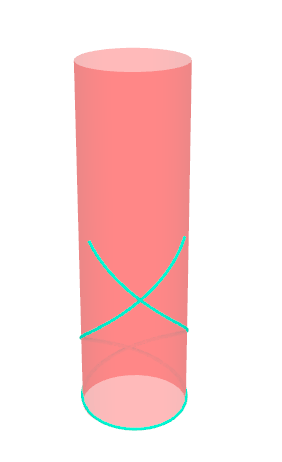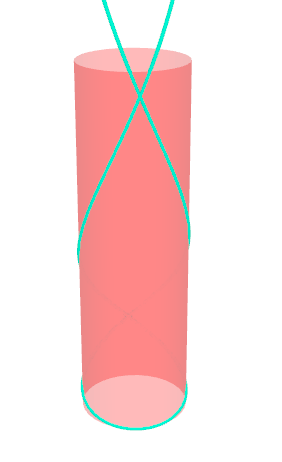
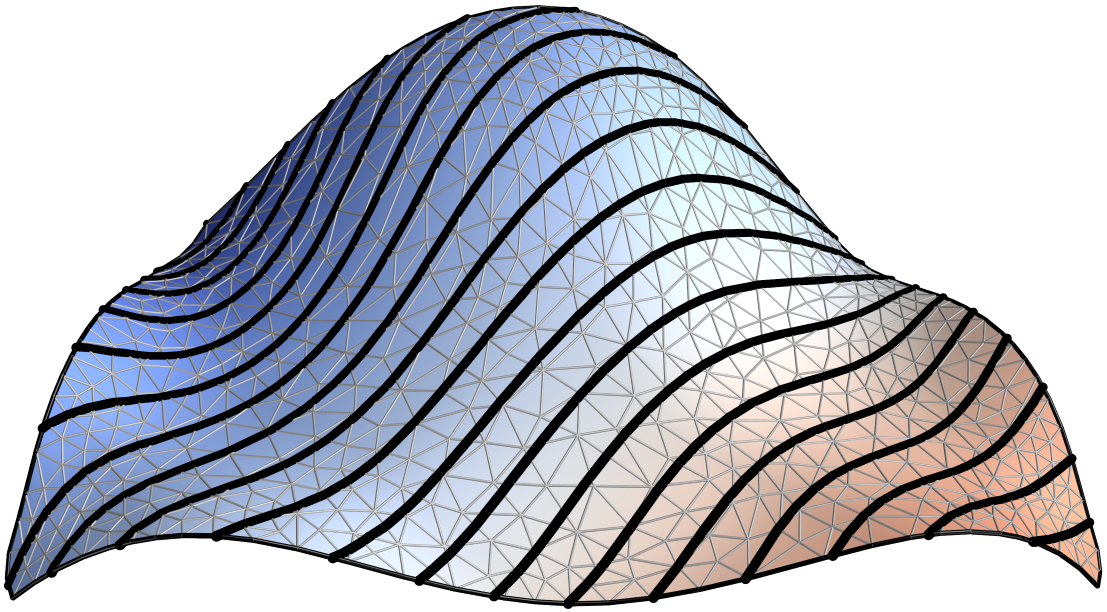
Video
TBD…
Code
Level-sets code see here.

Quad mesh optimization code see (TBD….)
